Implications Of ICD-10 Coding For Metastatic Renal Cell Carcinoma
What is Metastatic Renal Cell Carcinoma?
Metastatic renal cell carcinoma (mRCC) is a type of kidney cancer that has spread from the kidney to other parts of the body. It is the most common type of kidney cancer in adults, accounting for approximately 90% of all cases. The cancer typically begins in the lining of the tubules in the kidney and can spread to nearby lymph nodes, as well as to distant organs such as the lungs, bones, or liver.
Code Information
The ICD-10 code for metastatic renal cell carcinoma is C64.9. This code is used to classify and code diagnoses related to mRCC in medical records and billing processes. It is important for healthcare providers to accurately code mRCC to ensure proper treatment and reimbursement for services rendered.
Diagnostic Related Groups (MS-DRG)
Metastatic renal cell carcinoma falls under MS-DRG 673 – Kidney and Urinary Tract Cancers with Major Operating Room Procedure. This DRG is used to group together patients with similar diagnoses and treatments for the purpose of reimbursement by Medicare and other insurance providers.
Convert to ICD-9 Code
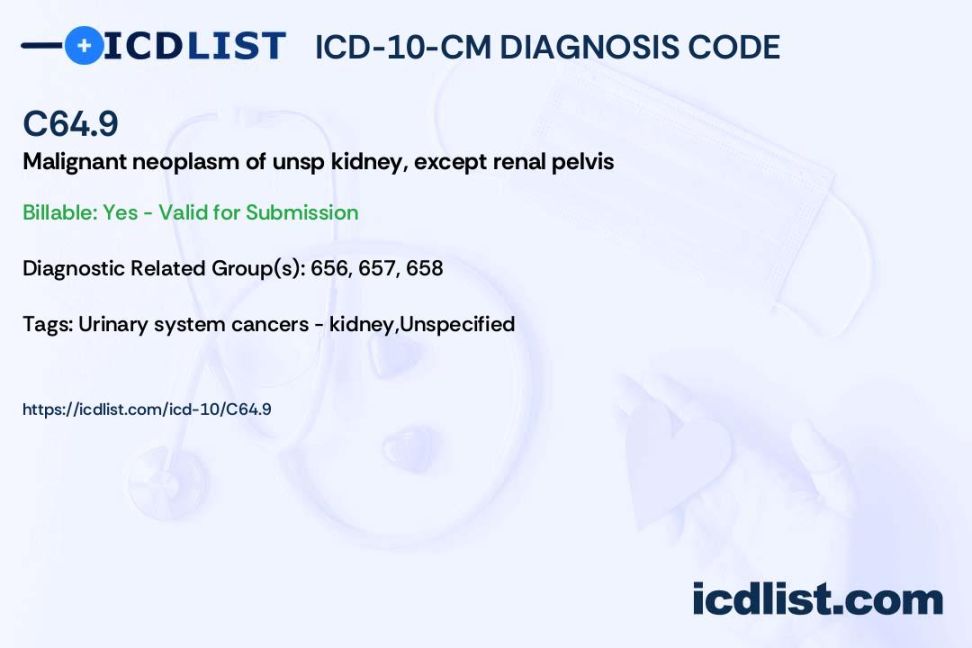
Prior to the implementation of ICD-10, metastatic renal cell carcinoma was classified under ICD-9 code 189.0. Healthcare providers should be aware of this conversion when reviewing historical medical records or coding for older cases.
Code History
The ICD-10 code for metastatic renal cell carcinoma, C64.9, was introduced in October 2015 as part of the updated coding system. This code replaced the previous ICD-9 code 189.0 for mRCC, providing a more specific and detailed classification for this type of kidney cancer.
Approximate Synonyms
Other terms that may be used interchangeably with metastatic renal cell carcinoma include advanced kidney cancer, stage IV kidney cancer, and renal cell cancer with metastasis. These synonyms may appear in medical records, research studies, or clinical discussions related to mRCC.
Clinical Information
Metastatic renal cell carcinoma is known for its resistance to traditional cancer treatments such as chemotherapy and radiation therapy. Targeted therapies and immunotherapies have shown more promising results in managing mRCC and improving patient outcomes. Common treatment options for mRCC may include surgery, immunotherapy, targeted therapy, and clinical trials.
Causes
The exact cause of metastatic renal cell carcinoma is not fully understood, but certain risk factors may increase the likelihood of developing this type of kidney cancer. These risk factors include smoking, obesity, high blood pressure, family history of kidney cancer, and genetic conditions such as von Hippel-Lindau syndrome.
Symptoms
Patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma may experience symptoms such as blood in the urine, back pain, weight loss, fatigue, fever, and swelling in the legs. These symptoms may vary depending on the location and extent of the cancer spread in the body.
Diagnosis
Diagnosing metastatic renal cell carcinoma typically involves a combination of imaging tests, blood tests, and a biopsy of the affected tissue. Imaging tests such as CT scans, MRIs, and PET scans can help determine the size and location of the cancer. Blood tests may measure levels of certain proteins or markers that indicate the presence of mRCC. A biopsy involves removing a small sample of tissue for examination under a microscope to confirm the diagnosis.
Treatment
The treatment approach for metastatic renal cell carcinoma may vary depending on the stage of the cancer, the patient’s overall health, and other individual factors. Surgery to remove the kidney (nephrectomy) or metastatic tumors, targeted therapies that block specific pathways involved in cancer growth, immunotherapies that boost the body’s immune response against cancer cells, and clinical trials testing new treatment options are all potential options for managing mRCC.
Conclusion
Metastatic renal cell carcinoma is a challenging type of kidney cancer that requires a comprehensive approach to diagnosis and treatment. Healthcare providers should be familiar with the ICD-10 code C64.9 for mRCC and stay updated on the latest advancements in managing this disease. Early detection and personalized treatment plans are key to improving outcomes for patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma.
FAQs
1. Is metastatic renal cell carcinoma curable?